Offboarding can feel like a scramble: IT racing to disable accounts, HR chasing signatures, and managers juggling knowledge transfer, all while trying to leave departing team members with a positive last impression. That’s where automation steps in to save the day.
By integrating your HR system, IT tools, and document workflows, you can transform a disjointed chore list into a streamlined, reliable process.
No more forgotten passwords or loose ends, just a predictable sequence that kicks off the moment someone’s status changes, revokes access across every platform, triggers exit surveys, and archives essential records.
In the following sections, we’ll unpack why automating offboarding isn’t just about ticking boxes. You’ll see how it strengthens security, reduces manual errors, and even helps capture valuable insights before employees move on.
We’ll walk through the key components of a solid workflow, weigh pros and cons, explore advanced enhancements, and share a clear roadmap to get you started. By the end, you’ll have a practical blueprint to streamline your own offboarding experience.
Key Takeaways
- Offboarding automation reduces errors, boosts security, and saves time.
- Integrating HRIS, IAM, and document workflows ensures consistency.
- Tools like Entra, BetterCloud, and Nudge offer turnkey automation.
- Metrics like access revocation time and audit readiness help prove ROI.
- A structured roadmap with pilots and refinement drives successful rollout.
Automated Offboarding
Automated Employee Offboarding refers to the process of using technology-driven workflows to manage every aspect of an employee’s departure, from disabling system access and recovering assets to conducting exit interviews and maintaining audit logs.
Instead of relying on manual checklists and cross-department coordination, automation ensures consistent execution of all necessary steps once an employee’s departure is initiated.
Typically initiated by a trigger in the HR system (like marking an employee as “inactive”), the workflow can:
- Automatically revoke access across digital platforms and facilities
- Generate and securely store termination documents
- Send notifications to IT, finance, and facilities teams
- Schedule exit interviews and collect feedback
- Log every action with timestamps for audit and compliance
By transforming offboarding into a streamlined, reliable process, organizations reduce the risk of data exposure, save valuable time, uphold compliance, and offer departing employees a respectful and organized exit.
Key Benefits of Offboarding Automation
Automating the offboarding process transforms a complex, multi-step chore into a smooth and reliable operation. It not only accelerates routine tasks like account deactivation and document handling but also strengthens security, ensures compliance, and preserves valuable knowledge.
Let’s explore the specific advantages that make offboarding automation a game-changer.
- Enhanced Security & Risk Reduction: Automating offboarding ensures that access is revoked immediately across all systems, minimizing data leakage and insider threats. Organizations report that manual offboarding can take over 21 days, while automation reduces this to mere minutes, significantly lowering the risk of credential misuse.
- Consistency & Accuracy: A guided, automated workflow guarantees that every step, such as revoking accounts, collecting assets, and generating forms, is handled reliably and uniformly. This eliminates human error and ensures full compliance with corporate and regulatory standards.
- Time & Cost Savings: By removing repetitive manual tasks, HR and IT teams regain countless hours and often reclaim unused software licenses automatically. Manual offboarding often clogs HR time with coordination; automation handles notifications, asset recovery, and documentation efficiently.
- Streamlined Documentation & Audit Trails: Automatically generated documents such as termination letters, NDAs, and clearance forms are securely archived. Each action is logged with timestamps, simplifying audits and supporting regulatory compliance.
- Knowledge Capture & Continuity: Automated offboarding includes steps for archiving files, transferring documents, and facilitating knowledge handovers. This preserves institutional memory and ensures incoming employees can pick up where others left off.
- Better Experience & Employer Branding: Smooth and respectful exits leave a positive impression. Automated offboarding not only triggers exit interviews and feedback but also fosters goodwill; departing employees often become vocal advocates.
- Scalability & Efficiency at Volume: Automation scales effortlessly as organizations grow. Whether processing one or ten resignations, the system executes reliable workflows, freeing teams from manual overload.
- Coordinated Communication: Automated notifications ensure that stakeholders such as managers, IT, payroll, facilities, and even external partners are informed in sync. This reduces confusion and keeps operations running smoothly.
Why Automate Offboarding?
Automating offboarding streamlines a complex process, triggering immediate account deactivation, asset collection, documentation, and notifications, so that no critical steps are missed or delayed.
This not only boosts consistency and security but also frees up HR and IT teams to focus on higher-value work while ensuring a professional and compliant exit experience.
01. Operational Efficiency
Manual offboarding often requires coordination across HR, IT, finance, and legal teams. Each step, such as sending forms, collecting hardware, and revoking access can become a time drain.
Automation can reduce this overhead dramatically. According to Nintex, automated workflows allow HR teams to simply trigger a process that handles the rest, saving significant time.
02. Security & Risk Mitigation
Leaving accounts active or missed credentials poses high risks. BetterCloud highlights that manual processes frequently overlook critical steps like resetting credentials or disabling sessions, leaving gaps exploitable by bad actors. Automation delivers consistency, and access is revoked uniformly and promptly.
03. Regulatory Compliance
In regulated industries, documentation of offboarding steps is vital. Automation platforms log each action that triggered it, when, and what was executed, providing a clear audit trail.
04. Improved Exit Experience
A chaotic offboarding can leave departing employees feeling undervalued. By contrast, a smooth exit, complete with structured knowledge capture and swift responses, preserves goodwill and enhances employer reputation.
Core Components Of An Automated Offboarding Workflow
To effectively automate offboarding, your workflow must include several key components that address access control, documentation, and accountability.
At its core, this means automating user deprovisioning through HRIS-IDM integration, managing role-based access control, handling document and asset workflows, and maintaining end-to-end audit trails for compliance.
These foundational elements ensure every offboarding step runs consistently, securely, and transparently.
A comprehensive offboarding automation framework should address several critical areas:
01. HR Trigger & Orchestration
Automation begins with a reliable trigger, typically when HR marks an employee as “inactive” in the Human Resource Information System (HRIS) or submits a separation request through the internal ticketing system. This event sets the entire offboarding workflow into motion.
02. Access De-provisioning
The system should automatically deactivate access to:
- Active Directory and corporate email accounts
- SSO-managed and OAuth-connected platforms (e.g., Google Workspace, Slack, Zoom)
- VPN credentials, SaaS tools, and cloud storage services
This step protects the organization from unauthorized data access and ensures compliance with internal security policies.
03. Credential & License Revocation
Once the offboarding trigger is initiated, the workflow should revoke application credentials, reset passwords, remove unused licenses, and disable multi-factor authentication (MFA) tokens across all platforms.
04. Document Handling
HR documentation, including termination letters, NDAs, tax documents, and clearance forms, can be automatically generated and securely archived. This ensures consistency and relieves HR teams from repetitive administrative tasks.
05. Asset Recovery & Knowledge Transfer
Automated systems can schedule equipment returns (e.g., laptops, ID badges, phones), notify IT or facilities teams, and initiate knowledge transfer checklists for project handoffs, SOP documentation, or password sharing.
06. System Notifications & Communication
Stakeholders such as IT, payroll, facilities, direct managers, and compliance officers should receive automatic updates about offboarding deadlines and responsibilities. This coordination avoids gaps in access, compensation, and facility handovers.
07. Exit Interviews & Feedback Collection
Automated tools can trigger surveys, schedule interviews, or launch AI-powered sentiment analysis forms to capture valuable insights from the departing employee. This feedback supports workforce planning and cultural improvement efforts.
08. Audit Trail & Reporting
A robust automation platform maintains a timestamped log of all offboarding actions. These records are crucial for audits, legal compliance, and tracking internal performance metrics related to employee exits.
Employee Offboarding Improvements with Automation
Pros & Cons Of Automation
Evaluating automation means weighing its power to eliminate errors, save time, and strengthen compliance against potential drawbacks like setup complexity and hidden costs.
While automated offboarding brings consistency, auditability, and improved security, organizations must consider the initial investment in mapping workflows, managing exceptions, and maintaining integrations.
That careful assessment ensures the gains outweigh the overhead.
| Pros | Cons |
| Time savings and process consistency—HR and IT no longer juggle ad-hoc tasks | Initial setup complexity—requires mapping workflows and coordinating teams. |
| Enhanced security—automated account deactivation reduces insider risk | Special case handling—not every scenario is standard; exceptions need manual oversight. |
| Stronger compliance—complete logs support audits and regulatory review | Tooling costs—automation platforms and integrations can be expensive. |
| Positive exit experience fosters goodwill | Ongoing upkeep—periodic reviews required to reflect SaaS changes. |
| Knowledge preservation—easy sharing of SOPs or project data | Data dependency—accurate HR data is critical for effective automation. |
Advanced Enhancements
Beyond basic workflows, advanced automation overlays intelligent layers, like AI, RPA, and adaptive logic, to handle complex, variable, and unstructured scenarios.
These enhancements enable your offboarding process to evolve from simple rule-based flows into proactive, context-aware systems that learn, detect edge cases, and scale across increasingly sophisticated environments.
- AI‑Enhanced Feedback Analytics: Leverage AI to analyze exit interview data. Identify patterns, such as cultural issues, leadership concerns, and trigger alerts, to inform HR of actions to take.
- RPA for Complex Systems: Use Robotic Process Automation to interact with legacy systems that lack APIs (e.g., payroll or helpdesk software), ensuring they’re integrated into the workflow.
- Adaptive, Role-Based Workflows: Different roles may require tailored offboarding (e.g., contractors, executives). Advanced platforms adapt workflows dynamically based on HRIS role metadata.
- SaaS Discovery & Cleanup: Modern SAAS sprawl means unauthorized apps proliferate. Tools like Nudge Security automatically discover OAuth and unmanaged SaaS accounts and help revoke access.
Implementation Roadmap
A clear roadmap helps you phase your automation strategically, establishing groundwork, building integrations, and refining based on feedback. This approach ensures your offboarding solution evolves in manageable stages with measurable impact.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to rolling out automated offboarding:
Step 1. Map Your Existing Offboarding Process: Visualize each task, such as access removal, hardware retrieval, documentation, notifications, and identify who is responsible.
Step 2. Identify Automation Opportunities: Focus on high-risk or manual-heavy tasks: account revocations, document generation, feedback triggers, etc.
Step 3. Select Automation Tools: Evaluate suites offering governance, HRIS integration, RPA, and SaaS discovery features, such as Microsoft Entra, Workato, BetterCloud, Nudge Security, ServiceNow, etc..
Step 4. Build and Configure Workflows: Start with a simple template (like Entra’s “scheduled leaver” flow), then tailor steps for your system integrations.
Step 5. Pilot with a Small Group: Choose a subset of employees or a pilot team to test the workflow. Monitor for accuracy, completeness, and user satisfaction.
Step 6. Refine and Expand: Adjust workflows based on pilot feedback. Add handling for edge cases or manual review steps as needed.
Step 7. Full Launch & Monitoring: Roll out across the organization. Use dashboards to track offboarding times, completion rates, feedback scores, and audit results.
Step 8. Continuous Improvement: Review quarterly, such as update workflows, add newly introduced applications, check feedback trends, and optimize.
Real‑World Examples & Tools
Implementing offboarding automation is easier when you know what tools to trust. These platforms offer robust capabilities to handle access deprovisioning, documentation, asset management, and audit compliance, each tailored to modern IT-HR environments.
01. Microsoft Entra Lifecycle Workflows
A template-based system that integrates with Azure Active Directory. It allows companies to automatically revoke Teams access, remove licenses, and delete user profiles based on predefined offboarding triggers.
02. Workato + Workday + ADP Integration
Workato connects HR platforms like Workday with systems such as ADP and ITSM tools to create unified workflows. It streamlines multistep processes like deprovisioning, payroll notification, and manager updates.
03. BetterCloud for SaaS App Coordination
BetterCloud focuses on orchestrating SaaS lifecycle management. It automates tasks such as user deactivation, orphaned access alerts, password resets, and compliance logging across tools like Slack, Google Workspace, and Box.
04. Nudge Security, SaaS Discovery & Cleanup
Nudge Security helps discover unmanaged OAuth connections and shadow IT. It automatically revokes app permissions, resets credentials, transfers ownership of assets, and ensures proper exit cleanup with a full audit trail.
05. HR Cloud & ServiceNow HRSD
These platforms offer structured offboarding frameworks, such as checklists, timed notifications, equipment return logs, and exit surveys, all visible from a centralized HR service dashboard.
06. BetterCloud for SaaS App Coordination
BetterCloud orchestrates user deprovisioning across SaaS, automates password resets, flags orphaned access, and logs changes.
07. Nudge Security SaaS Discovery
Detects unmanaged OAuth apps, offers password reset, revokes access, transfers ownership, and orchestrates cleanup tasks with a complete audit trail.
Best Practices For Success
To ensure your offboarding automation delivers real value, it’s crucial to follow proven best practices from early planning and tailored workflows to transparent communication and thorough documentation.
This approach not only protects data and supports compliance but also preserves positive relationships with departing employees.
- Begin the process early and communicate clearly with all stakeholders such as including IT, payroll, and managers, well before the departure date
- Maintain accurate inventories of devices and credentials to ensure complete recovery and prevent unauthorized access post-departure
- Use detailed, role-based offboarding checklists to ensure no step is missed, tailored to departure type and seniority
- Automate account disabling immediately upon trigger to eliminate security risks linked to delays in access revocation
- Send templated notifications across HR, IT, facilities, and management to coordinate tasks and maintain transparency
- Capture knowledge transfer through structured handoffs and documentation to preserve institutional memory and maintain continuity
- Conduct exit interviews or surveys automatically to gather actionable feedback and surface patterns in the turnover rationale
- Ensure comprehensive audit trails by logging each automated action with timestamps and details for compliance validation
Navigating Challenges & Pitfalls
Navigating the complexities of automated offboarding requires more than just deploying tools; it demands strategic awareness of potential pitfalls. Common challenges include rigid systems that don’t adapt to unique use cases, data security vulnerabilities, and gaps in human interaction and compliance.
Recognizing these issues upfront allows you to design an automation strategy that remains flexible, secure, and employee-friendly.
- Legacy systems: Older, non‑API tools don’t support automated workflows, necessitating the use of RPA bots or manual steps mapped separately to ensure full coverage.
- Shadow IT: Hidden SaaS accounts and OAuth permissions are often missed during termination, so use discovery tools that continuously map and deprovision these rogue access points.
- Role‑specific variation: Executives or IT staff often require customized offboarding, so design conditional workflows that adapt based on user role and privilege level.
- Change management: If stakeholders in HR, IT, and business units aren’t aligned early, automation fails, so communicate roadmap timelines and benefits upfront to ensure buy‑in.
- Tool costs: Automation licenses can be expensive, so calculate ROI by benchmarking reductions in risk, manual labor, exit time, and licensing waste before committing.
Measuring ROI
To demonstrate the real value of offboarding automation, start by defining clear metrics, like cost per offboarding and time to revoke access, so you can compare before-and-after performance.
Tracking improvements in security, process efficiency, and employee feedback helps build a compelling business case for ongoing investment.
Here are key metrics for Measuring ROI of offboarding automation and how to evaluate them effectively:
- Cost per Offboarding: Compare current cost (e.g., $2,500) to automated baseline (e.g., $1,200), demonstrating ~52% savings.
- Time to Revoke Access: Track reduction from manual delays (e.g., 4 days) to under 1 hour, highlighting efficiency gains.
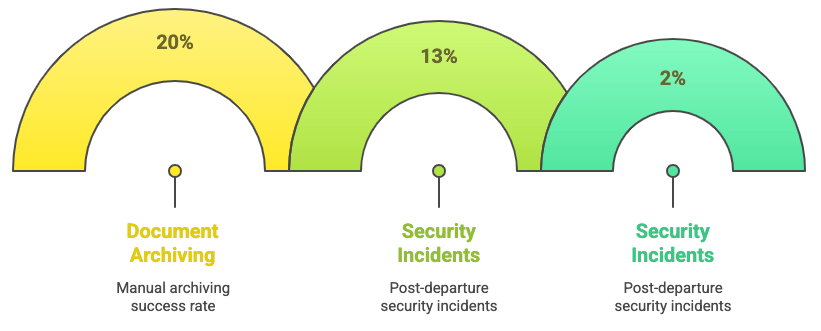
- Document Archiving Rate: Measure increase in successors receiving documents (e.g., from 20% to 85%), improving continuity.
- Security Incidents: Record decline in post-departure access or data misuse (e.g., severance disputes drop from 13% to 2%).
- Hours Saved / FTE Equivalent: Total hours automated scaled to FTE cost, e.g., 75h saved/month translates to $4,500/month savings.
- Process Velocity Improvement: Measure task speedup (e.g., 110% faster processing), directly indicating productivity gains.
- Compliance & Error Reduction: Track fewer missed tasks or errors, improved audit results and reduced compliance risks.
- Exit Feedback & Offboarding Score: Monitor completion of exit surveys and satisfaction ratings, which reflect experience quality.
By capturing these metrics, such as cost, time, security, compliance, and satisfaction, you can build a compelling ROI case and continuously refine offboarding processes.
Conclusion
Automating offboarding isn’t just about saving time; it’s a strategic safeguard that strengthens your security, compliance, and employer brand. With rapid SaaS adoption, increasing digital vulnerabilities, and stricter regulations, having a seamless, fully audited exit process is vital.
It helps avoid costly breaches, nurtures trust with current and departing employees, and keeps operations smooth. By mapping your workflows, selecting tools that fit your tech stack, piloting carefully, and continuously refining through real feedback, you’ll design an offboarding process that not only prevents oversights but becomes a strategic strength.
This kind of organizational resilience turns a routine HR function into a competitive edge, enhancing trust, protecting data, and supporting long-term business health.