Your HRIS houses the crown jewels of employee data, payroll, social security numbers, and evaluations. If it’s not secure, your organization risks not just fines, but broken trust.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to evaluate your HRIS system’s security, from access controls to vendor compliance, so you can sleep at night knowing sensitive employee information is protected.
That means security isn’t optional; it’s essential. Whether you’re choosing a new system or giving your current one a check-up, it pays to evaluate carefully.
This article walks you through everything you need to assess: from access control and encryption to monitoring, patching, and incident response.
We’ll also explore data governance, usability, and how well your vendor supports real security. Each section highlights practical features, reveals warning signs, and offers questions to guide your evaluation.
Plus, in the end, you’ll find a handy checklist to ensure no critical element slips through the cracks. Before long, you’ll be confident that your HRIS isn’t just efficient, it’s trustworthy and robust.
Key Takeaways
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and least privilege to limit data access
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and risk-based authentication
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit using standards like AES-256 and TLS
- Monitor user activity with alerts and secure audit logs for accountability
- Apply patches promptly and harden system configurations to reduce risk
- Verify vendor security with certifications, audit reports, and breach protocols
- Implement data governance practices aligned with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA
- Maintain regular, encrypted backups and test recovery processes
Access Control & Authentication in HRIS Security
Effective access control and authentication are foundational pillars for securing an HRIS. They ensure that only the right people, in the right roles, can access sensitive data, and only in the ways they’re authorized.
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) & Least Privilege
RBAC remains the industry standard for managing user permissions. By defining roles, such as “Payroll Admin,” “HR Generalist,” or “Manager”, and mapping specific privileges to each, RBAC ensures consistency and efficiency.
According to a NIST-acknowledged model, RBAC supports the separation of duties and simplifies permission management in large organizations.
Complementing RBAC, the principle of least privilege mandates that users only have access essential to their role. This not only limits the impact of compromised accounts but also minimizes internal misuse.
Best practice dictates periodic access reviews, ideally biannually, to remove obsolete permissions and reinforce compliance.
2. Multi-Factor & Risk-Based Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds a critical secondary layer, be it TOTP, SMS, biometrics, or hardware tokens, to strengthen traditional passwords. Studies show MFA reduces account compromise by over 99%.
Beyond static MFA, risk-based authentication evaluates context, like IP address, device, or time, to prompt extra verification only when needed. This adaptive approach balances security with user experience.
3. Account Lifecycle & Privileged Access
Robust provisioning and de-provisioning processes prevent orphaned or excessive privileges. Automated workflows tied to HR events (hire, transfer, exit) are ideal.
For privileged or administrative accounts, dedicated identities, monitored and rotated, should be enforced. In practice, IT should only receive elevated access when necessary, with HR retaining control over sensitive data visibility.
Data Encryption & Protection in HRIS: Best Practices
Encryption turns readable information into ciphertext by applying algorithms like AES-256, ensuring that only holders of the correct decryption keys can restore the original data.
In an HRIS, this covers both data in transit, secured via TLS/SSL during network exchanges, and data at rest, protected within databases, file stores, and backups.
Complementary measures like field-level masking and tokenization replace or obscure sensitive elements (e.g., SSNs, salary figures) so that unauthorized viewers see only nonsensitive placeholders.
Robust key-management systems handle generation, storage, rotation, and access control for cryptographic keys. Together, these controls safeguard confidentiality, maintain integrity, and help meet regulatory requirements.
Why it matters
- Secure employee data: Protect sensitive information (e.g., SSNs, payroll) from breaches using strong encryption standards
- Prevent interception: Ensure data remains unreadable during transmission with TLS and SSL protocols
- Meet compliance requirements: Align with HIPAA, GDPR, and other mandates by encrypting data at rest and in transit
Real-Time Monitoring & Audit Trails in HRIS
Monitoring, alerts, and auditing refer to the systematic processes that track user activity, detect anomalies, and maintain secure records within an HRIS.
Monitoring continuously observes actions, like logins, data exports, or configuration changes. Alerts proactively notify administrators or security teams when suspicious behavior occurs (e.g., multiple failed logins or unusual access patterns).
Auditing preserves tamper‑resistant logs of who did what, when, and from where, providing a forensic account of system events.
Together, these mechanisms enable real-time threat detection, post‑incident investigation, compliance reporting, and operational oversight, ensuring visibility and accountability throughout the system.
Why it matters:
- Enable real-time threat detection: Spot unusual behavior and respond before issues escalate
- Support compliance and audits: Maintain tamper-proof logs to demonstrate regulatory compliance
- Enforce accountability: Track user actions clearly to detect internal misuse or negligence
Patch Management & Secure Configuration
Ensuring your HRIS is secure starts with disciplined patch management and system hardening. Timely patches close vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them, while secure configuration, like disabling default admin accounts, enforcing HTTPS, and locking down unnecessary services, reduces your system’s attack surface.
A centralized tool helps automate asset inventory, prioritize updates, test patches in staging, and roll out changes systematically.
Detailed documentation and the ability to roll back failed patches ensure stability and audit compliance. Together, these practices keep your HRIS both resilient and responsive to new threats, fitting elegantly within a proactive security strategy.
Why It Matters
- Reduce exposure to known exploits: Apply updates promptly to prevent attacks through unpatched vulnerabilities
- Strengthen system resilience: Disable default settings and harden configurations to limit attack vectors
- Ensure audit readiness: Document patch schedules and rollback plans to pass compliance checks with confidence
Security Assessments & Vendor Compliance
Security assessments evaluate both your HRIS platform and the vendor’s overall security stance. They typically include automated vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and thorough third-party audits.
Evaluations examine technical controls (like encryption, access control), incident response plans, business continuity, and compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
Vendor compliance involves verifying certifications, reviewing audit reports, and enforcing contractual security obligations, such as data breach notification timelines, right-to-audit clauses, and security SLAs.
Together, these practices confirm that both the software and the provider uphold strong security standards, reducing risk from third-party exposure.
Why It Matters
- Identify hidden risks: Conduct regular testing to uncover vulnerabilities before attackers do
- Verify trustworthiness: Validate vendor security practices with certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2
- Enforce contractual protection: Use security SLAs and audit rights to hold vendors accountable
Data Governance & Privacy
Data governance is the structured framework, such as comprising policies, roles, and processes, governing how employee data is collected, stored, accessed, and retained.
It ensures accurate, consistent, and secure handling of information throughout its lifecycle. Privacy components include consent management, data minimization, anonymization, and support for rights such as access and deletion, aligning internal practices with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
Together, these measures build trust, maintain compliance, and reduce risk.
Why it matters
- Improve data quality and control: Establish clear ownership and lifecycle management for employee data
- Avoid legal penalties: Align with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and other privacy regulations
- Support employee rights: Enable consent, access, and deletion in line with transparency and ethical use
Backup & Disaster Recovery Readiness for HRIS
Effective backup and incident readiness ensure your HRIS can bounce back from data loss, outages, or cyberattacks, with minimal damage and maximum confidence. Set up automated, encrypted backups stored in multiple locations (on-premises and off-site/cloud).
Regularly test restores in an isolated environment to catch corruption or ransomware. Meanwhile, maintain a clear incident response plan: define roles, establish communication protocols, and run tabletop drills.
Document step-by-step recovery procedures (playbooks) and include third-party vendor coordination. Together, these practices help you restore systems quickly, follow compliance rules, and safeguard your organization’s reputation and continuity, even during unexpected disruptions.
Why it matters:
- Minimize downtime and disruption: Restore data quickly after outages or attacks using tested backups
- Safeguard business continuity: Ensure encrypted backups are stored off-site and recoverable
- Ensure readiness for crises: Use incident playbooks and drills to respond swiftly and clearly during emergencies
Building a Security-First Culture in HRIS
Security must fit seamlessly into everyday HRIS use, and that starts with usability and a supportive culture. Usable security enables users to follow protective steps confidently, without frustration or shortcuts.
Meanwhile, a strong security culture ensures employees feel responsible for protecting data, speak up about oddities, and learn continually from mistakes.
When security is easy and everyone’s involved, your HRIS becomes reliably safe, not just technically secure, but practically resilient.
Why It Matters
- Reduce human error: Design user-friendly security processes that employees can follow confidently
- Encourage early reporting: Foster a culture where users flag suspicious activity without fear
- Drive long-term resilience: Empower teams with continuous security training and open communication
Common HRIS Security Red Flags to Watch For
The concise red flags below provide clear, practical indicators to watch for during HRIS evaluation or security reviews:
- Vendor gives vague or evasive security answers during evaluation or audits (clear transparency is key)
- No evidence of recent third-party security audits or compliance certifications (e.g., ISO, SOC‑2)
- Accounts without MFA or weak password policies are still in active use across the HRIS
- Sensitive data transmitted unencrypted or unmasked, exposing details in transit or at rest
- No logs, alerts, or auditing capability for critical actions like role changes or data exports
- Patches not applied promptly, leaving known software vulnerabilities open for exploitation
- Absence of data retention policies allows old, unnecessary personal records to accumulate indefinitely
- Backup systems are untested or unsecured, risking data loss or unauthorized recovery
- Users bypass security mechanisms due to poor usability or cumbersome workflows
- IT holds unrestricted HRIS access without documented role limits, audit trails, or oversight
HRIS Security Evaluation Checklist
It’s helpful to use a structured framework that clearly defines each security domain and the specific questions you should ask vendors.
This checklist guides you through essential areas, from access control to incident response, so you can assess your HRIS thoroughly and confidently.
| Security Area | Questions to Ask / Test |
| Access Control | Are roles clearly defined? Is access audited regularly? |
| Authentication | Is MFA available and enforced? Is there risk-based auth in place? |
| Encryption | Are TLS and AES‑256 used? Are backups encrypted? |
| Audit Logging | Do logs record all access/modifications? Are alerts triggered appropriately? |
| Patch Management | Are updates automatic? How quickly do patches get applied? |
| Vulnerability Testing & Audits | Are scans and penetration tests performed consistently? Any certifications held? |
| Governance | Is data minimization enforced? Are privacy controls in place? |
| Backup & Recovery | Are backups regular, secure, and tested? Is there a tested recovery plan? |
| Incident Response | Are there documented breach handling procedures? Have drills been conducted? |
| Usability & Culture | Are users trained? Does security interfere with workflows? |
| Vendor Transparency | Are audit reports available? Does the vendor communicate openly? |
HRIS Security Best Practices & Expert Recommendations
It’s important to understand that effective HRIS security is never just a one-off task; it’s an ongoing, coordinated effort.
From robust access controls and encryption to vigilant monitoring and team involvement, aligning technical defenses with clear policies and human awareness creates a resilient system against evolving threats.
Keeping controls fresh, transparent, and user-friendly ensures your HRIS stays both compliant and secure.
- Enforce complex password policies and mandatory multi‑factor authentication to drastically reduce the risk of credential compromise
- Apply security patches promptly, ideally through automated deployment, to close emerging vulnerabilities before exploitation occurs
- Conduct vulnerability scans and penetration testing regularly to uncover weaknesses and reinforce your system’s defenses proactively
- Implement role‑based access control with least privilege and quarterly reviews to limit exposure and insider risks
- Encrypt all sensitive HR data, both in transit and at rest, using industry‑standard algorithms like AES‑256
- Maintain regular encrypted backups stored offline and test restores routinely to ensure reliable data recovery capabilities
- Monitor HRIS activity in real‑time, configure alerts for anomalies, and review logs to detect threats swiftly
- Provide ongoing security training and awareness programs to maximize user compliance and reduce human error vulnerabilities
- Institute data governance controls like minimization, retention policies, and pseudonymization to strengthen privacy compliance
- Establish an incident response plan with vendor SLAs and regular drills, enabling swift containment and remediation
HRIS Security Pillars
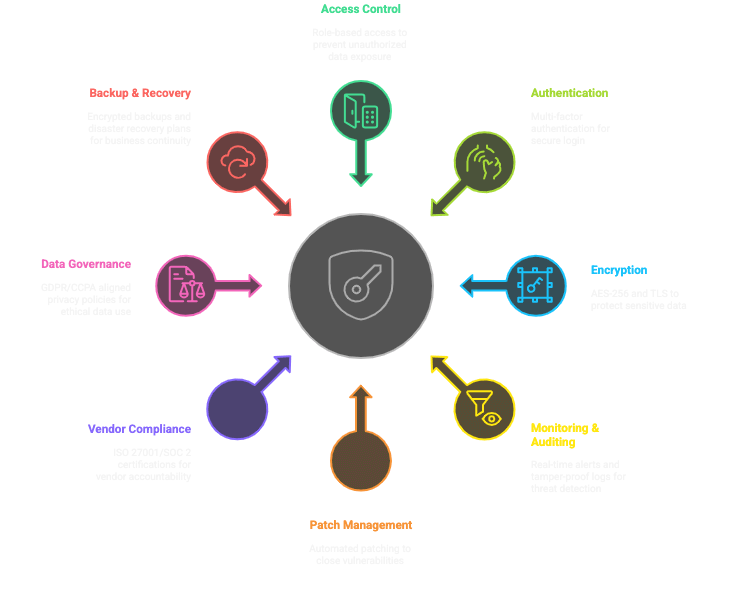

Final Thoughts on Securing Your HRIS
Protecting employee data isn’t just about ticking compliance boxes; it builds trust with your workforce and enhances your organization’s resilience against growing threats.
A secure HRIS isn’t only technically sound; it signals to employees and stakeholders that their privacy matters, which directly impacts morale, engagement, and reputation.
By methodically evaluating authentication, encryption, audit trails, data governance, and cultural readiness, you reinforce both operational efficiency and stakeholder confidence.
Use the provided checklist to guide vendor selections or conduct thorough internal audits, ensuring no aspect of security is overlooked.
When technical defenses align with usability and organizational commitment, your HRIS stops being merely a tool; it becomes a trusted foundation. That’s when your system truly empowers, not exposes, your people and your brand.








